Breast cancer is a disease that starts in the breast. Normally, when cells grow old or are abnormal they die off as the body creates new cells to replace them. However, cancer develops if this process is altered by anything where your body keeps making new cells while the old and abnormal cells are not dying off as they should.
As the cancer cells continue to accumulate, they can crowd out normal cells forming lumps(solid tumours) that hinder the body from working the way it should.
Breast cancer grows in stages:
- Stage 1 and 2 cancer has not spread through the whole breast.
- Stage 3 and 4 cancer has spread through the entire breast and to nearby organs.
If breast cancer is discovered in the early stages, a better outcome is expected and Knowing the stage helps in choosing the best treatment.
What are the causes?
The cause of breast cancer is not known but there are rather factors that put certain individuals at a greater risk of developing breast cancer than others which include;
- Genetics: Having a family history of breast cancer among close relatives.
- Gender: Females are more likely to develop breast cancer than males.
- Age: The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age
- Women that have never given birth in their life are at a greater risk than those that have given birth.
- History of having breast cancer in one breast.
- History of chest radiation exposure for example X-Rays
- Obesity
- Postmenopausal hormonal therapy
- Lifestyle: Risk increases among smokers more than non-smokers.
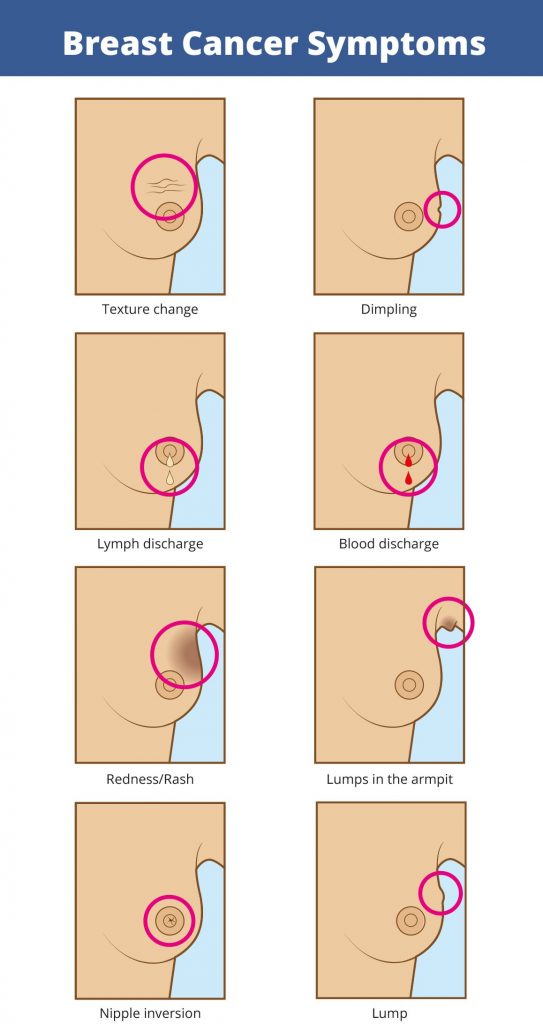
Signs and symptoms:
- A lump in the breast.
- Swollen lymph nodes under armpits.
- Changes in the breast skin appearance i.e dimpling or wrinkling.
- Inverted nipples.
- A notable change in the size and shape of the affected breast i.e it will be bigger than normal.
- An abnormal discharge from the nipples, sometimes it could be blood.
- Unexplained drastic weight loss.
- Redness/flaky skin in the nipple area.
How to self diagnose:
Breast cancer in both men and women can be detected earlier through routine self-breast examination which involves two aspects:
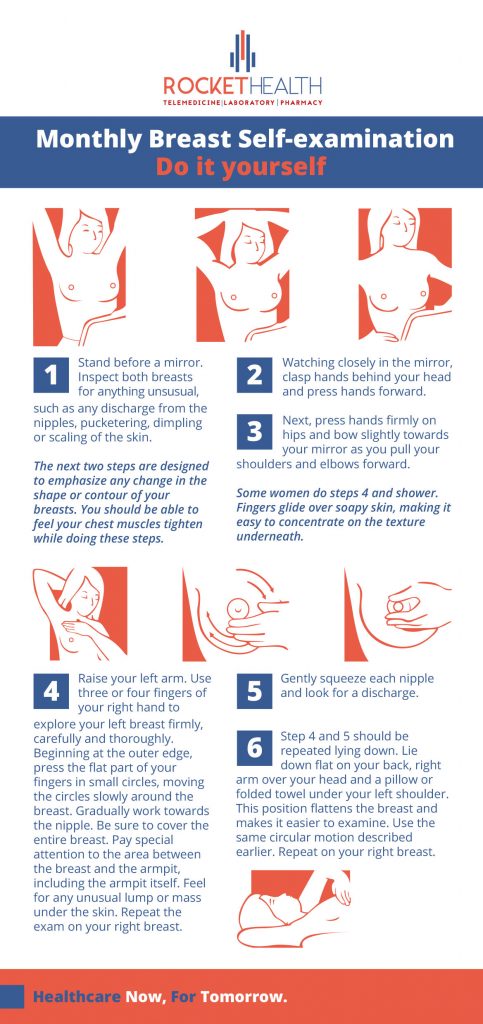
Inspection:
Stand in front of the mirror, with your hands pressed on your hips, observe the breast for any changes in the skin appearance, changes in shape and size of the breast, the appearance of the nipples.
With your hands raised over the head and palms held together, observe if the ridges along the bottom are symmetrical. Lower your hands slowly and observe critically if both breasts descend at the same time. A breast with a lump will descend faster than the one without a lump.
Manual examination:
Use your hands to manually examine your breast with your 3middle fingers. The aim is to feel for all the breast tissue following a uniform pattern so that the entire breast is covered:
While lying down, move your hands starting from the nipple moving outward to cover the entire breast following a circular motion. Repeat this while standing up preferably while in the shower with soap applied, this makes it easier for the examining fingers to easily slide over the skin and feel for any masses.
Effects of breast cancer if not diagnosed early:
If breast cancer is left undiagnosed, it means that early initiation of treatment during the early stage of the disease is impossible and so cancer will keep growing into advanced stages leading to:
- Cancer-related pain.
- Excessive weight loss.
- Cancer can spread to nearby organs (through the lymphatic system and bloodstream) like the lungs, lymph nodes, liver, and bones. Complications will arise in the functionality of these organs too.
- Reduced productivity.
- Depression among others.
Treatment for Breast cancer
The choice of treatment for breast cancer depends on the stage at which it is diagnosed and your general health as an individual. The earlier the diagnosis, the more successful the treatment process will be. Treatment methods include;
- Surgery involves cutting out cancer tissue.
- Chemotherapy involves using special medicines to kill cancer cells.
- Hormonal therapy blocks cancer cells from getting the hormones they need to grow.
- Radiotherapy involves using high dose radiations to kill the cancer cells and shrink the lump.
Written by Hope Nakawuma, Rocket Health Clinical Officer
(Featured image: Courtesy of Stanford Children’s Health)


